방법 구상
- printf의 format을 체크
- %를 만나면 형식지정자를 확인
- 해당 형식에 맞는 함수를 가변인자로 들어온 값으로 호출
- Mandatory : 파싱 → 출력의 2단계로 구성
- Bonus : 파싱 → 처리 → 출력의 3단계로 구성
구현 과정
파싱
- format 파싱
- %가 나올때까지 그대로 출력
- type 파싱
- cspdiuxX% 중 하나가 나오면 출력
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
if (type == 'c') count = ft_print_char(va_arg(*ap, int)); else if (type == 's') count = ft_print_str(va_arg(*ap, char *)); else if (type == 'p') count = ft_print_ptr(va_arg(*ap, void *)); else if (type == 'd' || type == 'i') count = ft_print_dec(va_arg(*ap, int)); else if (type == 'u') count = ft_print_dec_unsigned(va_arg(*ap, unsigned int)); else if (type == 'x' || type == 'X') count = ft_print_hex(va_arg(*ap, unsigned int), type); else count = write(1, &type, 1); return (count);
- char형이 va_arg에서 int로 설정되는 이유?
메모리에는 값을 기록하는 과정에서 CPU 접근에 부하를 덜어주기 위해 바이트 패딩이라는 방법이 사용되는데, 이로 인해 4byte 단위로 메모리에 접근을 하게 된다. 따라서 자료형의 크기가 4byte 이하인 경우에는 4byte로 처리가 된다.
출력
- 각 자료형에 맞게 처리하여 출력
ft_printf.c
- 함수별 설명
- ft_printf: 가변인자 목록을 만들고 ft_parse_format에 format과 목록 포인터의 주소값(?)을 넘겨준다.
- ft_parse_format: 넘어온 format과 ap를 통해 서식지정자를 나타내는 문자인 %가 나오면 ft_parse_type에 다음문자와 목록 포인터의 주소값(?)을 넘겨준다.
- ft_parse_type: 넘어온 문자를 체크해서 대응하는 함수를 호출한다.
- format에 NULL이 들어오는 경우 클러스터 맥에서의 동작:
[1] 2556 segmentation fault ./a.out함수 구현: -1을 리턴해줘서 에러 발생을 알린다.
ft_parse_format
if (!*format) : format의 맨 마지막에 %만 있는 경우
ft_print_hex.c
- 함수 종류
- ft_print_ptr: 주소값의 앞부분인 0x를 출력하고 진수 변환하는 함수를 호출한다.
- ft_print_hex: 10진수를 16진수로 변환한다.
- ft_addr_to_hex: 주소값을 10진수 unsigned long long 자료형으로 받아서 16진수로 변환한다.
ft_print_ptr
ft_addr_to_hex((unsigned long)addr, 'x'); : void *형으로 받은 포인터를 unsigned long형으로 형변환한다.
unsigned long형을 사용한 이유?- 주소값은 32bit OS에서는 4바이트, 64bit OS에서는 8바이트를 차지한다.
- unsigned long 은 32bit 에서는 4바이트 64bit 에서는 8바이트가 되므로 주소값을 담기에 적합하다.
ft_print_dec.c
- 함수 종류
- ft_print_dec: int형으로 들어온 값을 10진수로 출력한다.
- ft_print_dec_unsigned : unsigned int형으로 들어온 값을 10진수로 출력한다.
ft_print_dec
- code1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
int ft_print_dec(int n) { int len; char *str; len = 0; ft_putnbr_fd(n, 1); str = ft_itoa(n); len = ft_strlen(str); write(1, str, len); free (str); return (len); }
- 문제점 : malloc 에러 처리 필요
- code2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
int ft_print_dec(int n) { int len; len = 0; if (n == -2147483648) return (write(1, "-2147483648", 11)); if (n < 0) { len += write(1, "-", 1); n *= -1; } if (n >= 10) len += ft_print_dec(n / 10); len += write(1, &"0123456789"[n % 10], 1); return (len); }
ft_print_dec_unsigned
재귀함수 사용
ft_print_char.c
- 함수 종류
- ft_print_char
- ft_print_str
기타
Makefile
병렬 실행 옵션
make -j n : job을 한번에 n개 실행하여 컴파일 속도가 빨라진다.
- 의존성 문제
re: fclean all: j옵션으로 컴파일 시, all이 fclean보다 먼저 실행될 수 있다. - 해결방법
1 2 3
re: make fclean make all
Test
main함수 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#include "ft_printf.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
write(1, "ft_printf: ", 11);
printf(", %d\n", ft_printf("%d", 42));
write(1, "printf: ", 8);
printf(", %d", printf("%d", 42));
}
- make로 생성된 libftprintf.a 실행하는법
main.c에 헤더 include 한 후에gcc main.c libftprintf.a로 컴파일 후 a.out 실행하여 사용
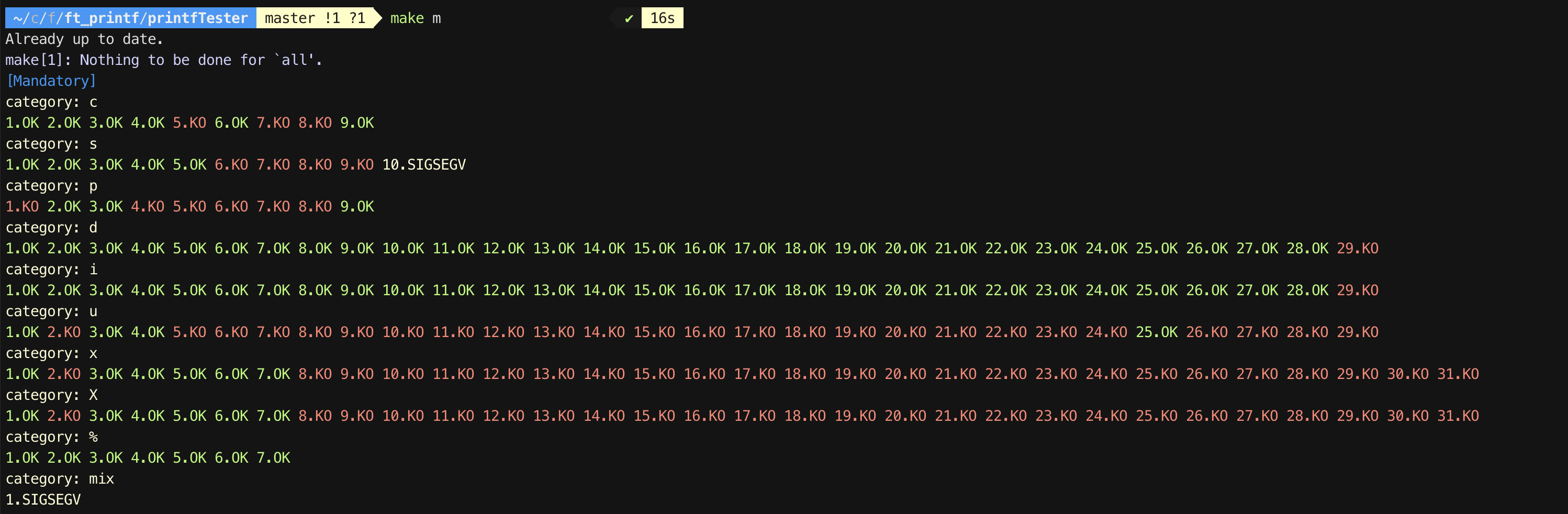
테스터
1. Tripoulle
https://github.com/Tripouille/printfTester
틀린 부분
- s
두번째 인자를 못받고 계속 첫번째만 받는다.
해결방법: 인자를 넘겨줄때 & 형태, * 형태로 넘겨준다. - u
len 변수가 누적되도록 더해주질 않는다. - d
ft_itoa 함수를 사용하고 메모리 해제를 하지 않는다. - h
len 변수가 누적되도록 더해주질 않는다. - x
자료형을 잘못 사용한다.
24,25, 27-291 2 3 4 5
TEST(24, print(" %x ", LONG_MAX)); TEST(25, print(" %x ", LONG_MIN)); TEST(27, print(" %x ", ULONG_MAX)); TEST(28, print(" %x ", 9223372036854775807LL)); TEST(29, print(" %x %x %x %x %x %x %x", INT_MAX, INT_MIN, LONG_MAX, LONG_MIN, ULONG_MAX, 0, -42));
2. ft_printf_tester
https://github.com/paulo-santana/ft_printf_tester
Ref.
https://supercoding.tistory.com/37
https://bigpel66.oopy.io/library/42/inner-circle/4
https://velog.io/@hkh406/ftprintf-%EC%A0%95%EB%A6%AC